Chapter 29 Iterator
Iterator is an class used to access elements of Vector DataFrame List. If you want to use algorithms provided by standard C++, you need to understand iterator. Because many of the algorithms provided by standard C++ use iterators to specify location or range of data to apply the algorithms.
Specific iterator type is defined for each data structure of Rcpp.
NumericVector::iterator
IntegerVector::iterator
LogicalVector::iterator
CharacterVector::iterator
DataFrame::iterator
List::iteratorThe figure below shows schematically how to access vector elements using an iterator.
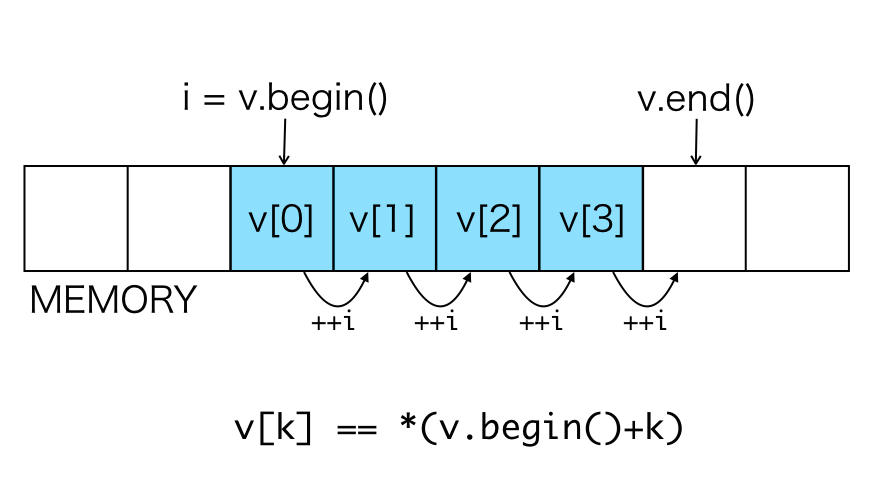
i = v.begin(): The iteratoripoints to the first element ofv.++i: Updatesito the state pointing to the next element.--i: Updatesito the state pointing to the previous element.i + 1: Represents the iterator pointing to the next element (one element afteri).i - 1: Represents the iterator pointing to the previous element (one element beforei).*i: Represents the value of the element pointed byi.v.end(): Represents an iterator pointing to the end (one after the last element) ofv.*(v.begin()+k): Represents the value of thek-th element ofv(v[k]).
The following code example shows an example of traversing all the elements of a NumericVector using iterator to calculate sum of the elements.